What is the most challenging task in the UK tax system? Every small accounting practice will know the answer, which is navigating self assessment tax returns. As 31st January comes close your clients will be in a state of panic to get the job done quickly making simple self assessment daunting and confusing.
All this confusion can be avoided if you keep your practice and your clients better organised in advance. In this blog, we will do that by breaking down Self Assessment, explaining who needs to file, showing how to complete a return efficiently and correctly, and outline who can support your practice in self assessment.
What Is Self Assessment Tax UK?
Self assessment is a system developed by HMRC for collecting income tax from individuals whose income is not taxed through the Pay As You Earn (PAYE) system. Under this process, liable persons, who aren’t on PAYE, must report their earnings, expenses, and allowances to the HMRC, which will calculate how much tax is owed.
Who Needs to File a Self Assessment Tax Return?
Not everyone is required to file a self-assessment tax return. However, it will apply to your client if they fulfil any one of the following points.
- Client is self-employed and income was over £1,000 per annum.
- Partner in a business partnership
- Freelancers or those with side jobs, earning additional income
- Money from renting out a property
- Tips and commission
- Income from savings, investments and dividends
- Foreign income
- Your client had to pay Capital Gains Tax when they sold or ”disposed of” something that increased in value.
Almost 11 million people submitted their self-assessment tax returns, and this number will rise this year.
How Does UK Self-Assessment Work?
There are multiple steps involved in the UK Self-Assessment process. These steps are:
Register for Self-Assessment
If your client is liable to file tax returns, they must be registered for self-assessment. The registration deadline is 5 October, and once registered, your client will not need to register again.
Completing and Filing Self-Assessment
After registration, you can file your client’s self assessment tax return online via the HMRC website or through accounting software. To complete and file a tax return, you will need to gather information like the following:
- UTR number
- Records of expenses
- Records of invoices
- Records of other business income
For limited company directors:
- their P60
- their P11D
The deadline for filing an online self assessment tax return with HMRC is 31 January, and for a paper tax return, it is 31 October.
Submit the Return
Submit your client’s self assessment online (preferably) or on a paper form. Use accounting software to file and submit the self-assessment directly.
Pay Your Tax
Once HMRC has processed your client’s return, they will inform you of the tax owed. This must be paid by 31 January following the end of the tax year.
How to Complete a Self Assessment Tax Return
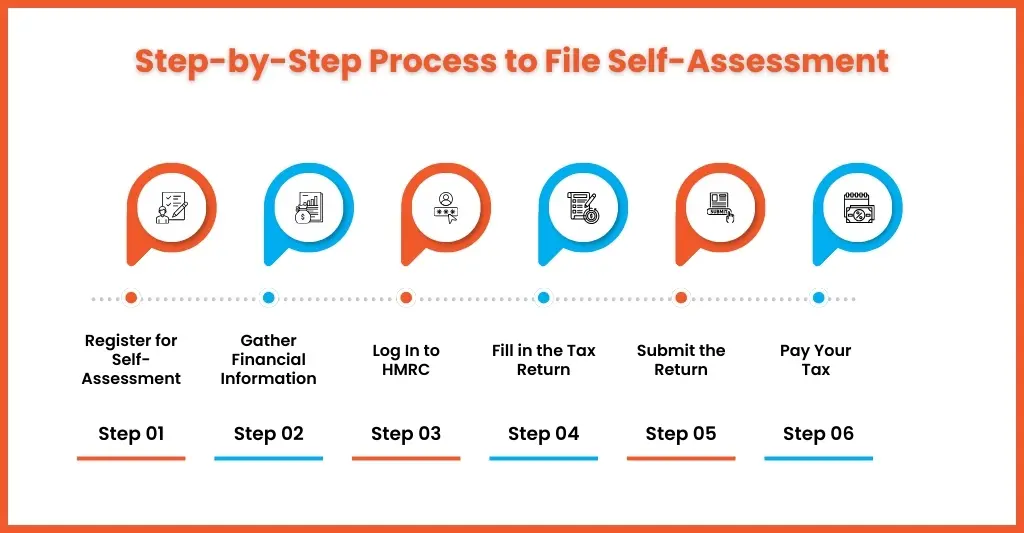
Completing a self-assessment for your client can get overwhelming for even experienced practitioners, but if you follow the right steps, it’s a simple process.
Register for Self-Assessment
Start by registering all your clients who are required to complete their self-assessment before the registration deadline. Once registered, HMRC will send a 10-digit Unique Taxpayer Reference number (UTR) within 10 days, along with an activation code. The UTR and activation code will be used to start your clients’ online self-assessment account.
The deadline to register for Self-Assessment is 5 October. You can skip it if your client is already registered.
Gather Financial Information
With registration out of the way, you can focus entirely on gathering financial information relevant to your clients, including:
- National Insurance number
- Records of income and allowable expenses if you are self-employed (invoices, receipts, accounts).
- Income from property rental, dividends, interest, foreign income, etc.
- Details of any taxable state benefits or pensions.
- Records of pension contributions.
- Records of charitable donations (Gift Aid).
Log In and Start Your Return
With the government gateway user ID and password in your hand, you can now sign in to the self assessment page. Once you have logged in, you will need to enter the relevant sections, such as:
SA100 (main section)
Under it, personal details of the client, such as date of birth, name, address, telephone number, and National Insurance number (updates in 2026), need to be added. Also, to be added are:
SA103 (self-employment)
Under this section, you report your client’s income from employment, such as a director’s salary. Employment benefits and expenses from the employment or directorship can also be declared.
SA105 (UK property)
This section needs to be filled if your client has received more than £1,000 from:
- Rental income and other types of income from UK land or property
- Income from letting out furnished rooms in your own home
- Income from furnished holiday lettings (FHL) in the UK or European Economic Area (EEA)
- Premiums from leasing UK land
- Inducements to take an interest in letting a property (a reverse premium)
Check for Errors and File Self-Assessment Tax Return
Once you’re done with all the sections, check it properly, especially the calculations. Any mistakes will lead to penalties, so always double-check. Once you have checked, save the copy and file the self assessment tax return.
Pay Tax Bill
If your client owes any tax to HMRC, then it is your responsibility to ensure that the payment is made by 31 January.
Self-Assessment Deadlines You Must Not Miss
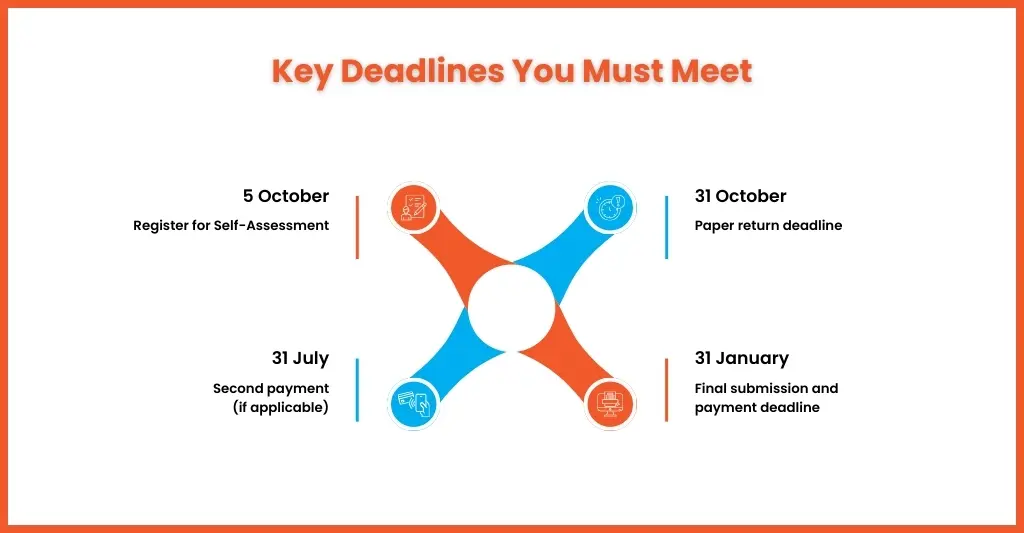
There are multiple deadlines associated with self-assessment, and missing them will be costly for your clients. Therefore, don’t miss the deadlines listed below.
- 5 October – Deadline to register for Self Assessment if it’s your first time filing
- 31 October – Deadline for paper tax returns
- 31 January – Final deadline for online Self Assessment submission
- 31 January – Deadline to pay tax owed for the previous tax year
- 31 July – Second payment on account (if applicable)
Missing the 31st January deadline will trigger instant penalties. These penalties can be avoided by preparing and filing on time.
Common Self-Assessment Mistakes UK Taxpayers Make
Mistakes in self assessment can create confusion, leading to penalties and unnecessary back-and-forth with HMRC. You must have come face-to-face with these mistakes year after year, and it is a source of great client stress. Hence, it is important to prevent your clients from making these mistakes at the first step before the deadlines.
Here are the most common Self-Assessment mistakes UK taxpayers make and why they matter.
Failing to Keep Adequate Records
Lack of records or improper record-keeping is one of the major sources of incorrect self-assessment tax returns. HMRC mandates taxpayers to keep their records for 5 years after the 31 January submission deadline. Without records, your client will be unable to prove their income and expenses, especially when HMRC demands evidence, leading to penalties.
Incorrectly Calculating Expenses or Claiming Ineligible Tax Reliefs
Making wrong relief claims is also a reality, and it invites more HMRC scrutiny. Some of the wrong claims include personal travel, home expenses, and mixed phone bills.
Missing Self-Assessment Deadlines
Frequent missing of self-assessment deadlines is a very common occurrence, especially among first-timers with multiple income sources. Hence, it is your practice responsibility to send reminders to your clients about the submission and payment deadlines. Such misses attract daily penalties and additional interest charges.
Omitting Income Such as Freelance or Rental Earnings
Many income sources, such as freelance work, side hustles, rental income, dividends, and overseas earnings, are often not declared. It must be noted that HMRC these days cross-checks data from banks, letting agents, and digital platforms. Any discrepancies between bank records and HMRC records will trigger investigations and penalties.
Confusing Personal and Business Expenses
It is a common mistake among sole traders and landlords, and it occurs when a single bank account is used for both personal and business spending. Separating these expenses becomes a tall ask, making returns harder to prepare. HMRC expect a clear separation, and any mixed records will lead to further scrutiny.
Penalties and Interest for Late Self-Assessment Filing
Missing the Self-Assessment deadline can lead to serious consequences, including:
- An initial £100 penalty
- After 3 months, additional daily penalties of £10 per day, up to a maximum of £900
- A further penalty of 5% of the tax due or £300, after 6 months, whichever is greater
- Another 5% or £300 charge after 12 months, whichever is greater
Can You Get Help With Self-Assessment?
In the past, accounting practices did not need any help when it came to handling self-assessment tax returns. However, with time, regulations and volume increased, leading to self-assessment becoming a time-consuming and resource-intensive task, creating problems for small accounting practices.
Professional accounting outsourcing service providers understood this problem and started offering their services. Their services enabled practices to reduce their workload.
Preparing for the Future of Self-Assessment in the UK
2026 is the year when self-assessment in the UK is going to change fundamentally. Make Tax Digital for Income Tax is going to be a reality, meaning instead of yearly self-assessment, there will be quarterly digital updates. It’s high time for you to embrace digital year end outsourcing services to be better prepared to handle this shift and provide a seamless experience for your clients.
People Also Ask
Can accountants file Self Assessment on my behalf?
Yes, accountants working in outsourcing firms are trained to handle self-assessment tax returns on your behalf. Their experience in maintaining compliance with HMRC laws and accuracy will increase your credibility.
How does a self-assessment tax return work?
Under self-assessment, a tax return must be filed for all the taxable income of the year, which does not come under PAYE, meaning it is not deducted directly.
How to complete a self-assessment tax return without errors?
Carefully vet all your clients’ documents, and if assistance is required, use professional outsourcing services.
What income must be declared under UK Self Assessment?
All income must be declared, including income from employment, self-employment, rental income, savings, investments, and any foreign income.
Conclusion
Guiding your clients in navigating self-assessment is crucial for staying compliant and avoiding penalties. Hence, you need to understand the workings of self-assessment returns, who needs to file, and their deadlines. This way, you can help your clients in meeting their tax obligations.
However, as mentioned above, managing self-assessment is no longer simple and will become increasingly stressful. For this reason, many practices are looking for outsourcing partners who can share the burden and offer value-adding self-assessment services for their clients, and Equallto checks that box.
Equallto is one step ahead of its competitors by offering MTD-compliant accounting services, keeping accounting practices future-ready and their clients safe from non-compliance and penalties.
Need help with Self-Assessment? Get in touch with Equallto today for professional tax return services that simplify the process and save you from costly mistakes.

